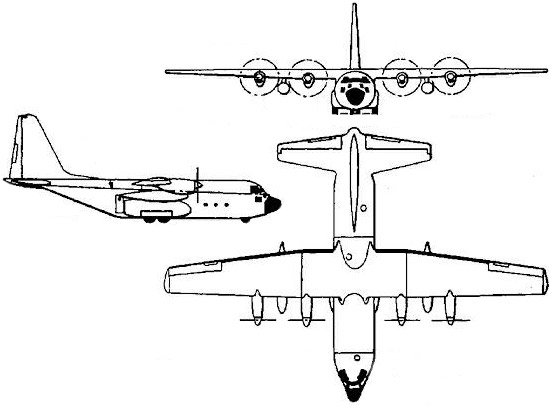
C-130 Hercules
Summary
| Category | Military Transport Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇺🇸 United States |
| Manufacturer | Lockheed |
| First flight | 23 August 1954 |
| Year introduced | 1956 |
| Number produced | 2500 units |
| Average unit price | $30 million |
Description
The C-130 Hercules is a military transport aircraft originally designed and produced by the American aerospace company Lockheed Martin. Its first flight took place on August 23, 1954. The aircraft was developed to meet a United States Air Force requirement for a versatile, robust, and long-range transport plane. Over time, the C-130 has been adapted for various roles and missions, but its primary function remains to transport troops, equipment, and supplies. It has seen service in numerous conflicts, humanitarian missions, and special operations around the world.
The C-130 Hercules features a high-wing, four-engine turboprop design that prioritizes durability, versatility, and the ability to operate from unprepared airstrips. Its distinctive high-wing configuration allows for greater ground clearance, which is particularly advantageous for cargo loading and unloading. The aircraft is powered by four Allison T56 turboprop engines, each driving a four-bladed propeller. The airframe is largely made of aluminum alloy, designed for both strength and weight efficiency.
One of the most distinguishing features of the C-130 is its rear-loading cargo ramp, which facilitates the quick loading and unloading of cargo, and enables airdrops. The cargo hold is spacious, capable of accommodating a variety of payloads including vehicles, troops, or medical supplies. Its flexible design allows for multiple configurations to suit different mission requirements.
The cockpit is designed for a crew of at least three: pilot, co-pilot, and loadmaster. More specialized versions might include roles for navigators or other specialized crew members. Advanced avionics and systems have been integrated into later models, improving navigational, communication, and safety features.
In terms of aerodynamics, the C-130 is not designed for speed but rather for versatility and lifting capability. Its wing and fuselage design allow for stable low-speed flight characteristics, crucial for airdrop missions or short takeoff and landing (STOL) capabilities.
Operational history
The C-130 Hercules has an extensive operational history that spans nearly seven decades, making it one of the longest-serving military aircraft in the world. After entering service with the United States Air Force in 1956, the aircraft quickly demonstrated its capabilities and adaptability, resulting in its widespread use by air forces globally.
The C-130 saw its first major combat deployment during the Vietnam War, where it served in various roles including troop and cargo transport, medevac, and even as a gunship in the AC-130 variant. Its performance in austere and challenging conditions solidified its reputation as a reliable and versatile transport aircraft.
In the subsequent years, the C-130 played significant roles in numerous conflicts and operations. During the Gulf War in 1990-1991, the aircraft was instrumental in airlifting supplies and personnel. It has also been involved in NATO operations in the Balkans, the war in Afghanistan, and the Iraq War, among others. Its adaptability was further highlighted by its use in special operations missions, including the 1976 Entebbe hostage rescue operation by Israeli forces.
Variants
Variants have been developed for specialized roles including aerial refueling (KC-130), electronic warfare, and surveillance, among others.
- C-130A/B/E/H: These are the basic cargo and troop transport variants that form the backbone of the C-130 fleet. They differ primarily in engine types and avionics. The "H" variant, in particular, is widely used and features updated turboprop engines and various improvements over earlier models.
- AC-130: Known as the "Spectre" or "Spooky," this is a heavily armed gunship variant. It's equipped with side-firing weapons such as cannons and howitzers and is used for close air support and force protection missions.
- MC-130: This variant is specialized for special operations missions, including infiltration, exfiltration, and aerial refueling of special operations helicopters. It includes versions like the MC-130E Combat Talon I, MC-130H Combat Talon II, and the MC-130J Commando II.
- KC-130: This is an aerial refueling variant, primarily used by the U.S. Marine Corps to refuel tactical aircraft and helicopters. It can also be used for cargo and troop transport.
- EC-130: This electronic warfare variant is equipped with various systems for psychological operations, command and control, and radar jamming. Notable subtypes include the EC-130H Compass Call, used for electronic attack, and the EC-130J Commando Solo, used for psychological operations and civil affairs broadcast missions.
- HC-130: Primarily used for search and rescue (SAR) missions, these variants are equipped with advanced radar, air-to-air refueling capabilities for helicopters, and other specialized equipment.
- LC-130: Adapted for polar operations, the LC-130 features ski-equipped landing gear that allows it to land on snow and ice. It is used by the U.S. Air National Guard for resupply missions to Antarctica and Greenland.
- C-130J Super Hercules: This is the latest production variant, featuring new Rolls-Royce AE 2100 D3 turboprop engines, a digital glass cockpit, and updated avionics. It's capable of higher speeds, greater range, and offers more efficient operations.
- SC-130J Sea Hercules: Proposed for maritime patrol and anti-submarine warfare roles, this variant is still in the conceptual stage.
Technical specifications
| Version: C-130H | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 2 pilots + 3 |
| Operational range | 8,375 km (5,204 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 593 km/h (368 mph) |
| Wing area | 162 m² (1743.8 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 40.4 m (132.7 ft) |
| Height | 11.7 m (38.3 ft) |
| Length | 29.8 m (97.9 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 10,058 m (32,999 ft) |
| Empty weight | 35,800 kg (78,925 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 70,307 kg (155,000 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 9.3 m/s (30.5 ft/s) |
| Takeoff distance | 1,093 m (3,586 ft) |
| Powerplant | 4 x turboprops Allison T56-A-15 delivering 3661 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
United States | 425 (+32) | |

|
Saudi Arabia | 33 | |

|
Iran | 28 | |

|
Canada | 25 | |
|
Indonesia | 25 | |

|
Egypt | 22 (+2) | |
|
Japan | 20 | |
|
Pakistan | 20 | |

|
Taiwan | 20 | |

|
Algeria | 18 | |

|
Turkey | 18 | |

|
France | 16 | |

|
South Korea | 16 | |

|
Morocco | 14 | |

|
Australia | 12 (+20) | |
|
India | 12 | |
|
Thailand | 12 | |

|
Malaysia | 10 | |

|
Colombia | 9 | |

|
Iraq | 9 | |
|
Italy | 9 | |

|
United Arab Emirates | 8 | |
|
Bangladesh | 8 | |

|
Israel | 8 | |

|
Jordan | 7 | |

|
New Zealand | 6 (+2) | |

|
Romania | 6 | |

|
Tunisia | 6 | |

|
Philippines | 5 (+5) | |
|
Poland | 5 (+5) | |

|
Argentina | 5 | |

|
Chile | 5 | |

|
Greece | 5 | |

|
Oman | 5 | |

|
Singapore | 5 | |

|
Sweden | 5 | |

|
South Africa | 5 | |

|
Bolivia | 4 | |

|
Denmark | 4 | |

|
Netherlands | 4 | |

|
Norway | 4 | |

|
Portugal | 4 | |
|
Qatar | 4 | |

|
Austria | 3 | |

|
Cameroon | 3 | |

|
Germany | 3 | |

|
Mexico | 3 | |

|
Niger | 3 | |

|
Peru | 3 | |

|
Venezuela | 3 | |

|
Bahrain | 2 | |

|
Ethiopia | 2 | |
|
Libya | 2 | |

|
Nigeria | 2 | |

|
Botswana | 1 | |

|
Ecuador | 1 | |

|
Gabon | 1 | |

|
Sudan | 1 | |

|
Chad | 1 | |

|
Uruguay | 1 | |
All operators