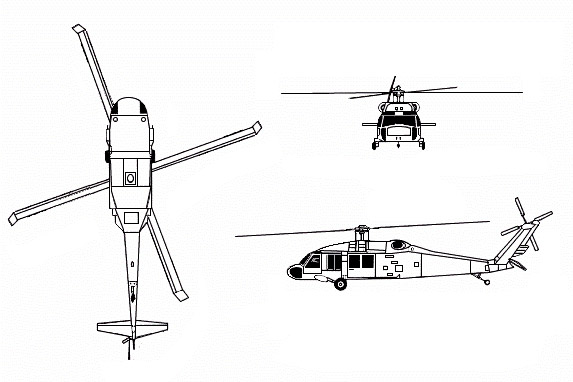
UH-60 Black Hawk
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇺🇸 United States |
| Manufacturer | Sikorsky |
| First flight | 29 November 1974 |
| Year introduced | 1979 |
| Number produced | 5000 units |
| Average unit price | $21 million |
Description
The UH-60 Black Hawk is a multi-role utility helicopter developed by Sikorsky Aircraft, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin. The Black Hawk was designed to meet the United States Army's requirement for a tactical transport helicopter to replace the aging UH-1 Huey in the late 1970s. The first flight of the UH-60 took place on November 29, 1974, and it was officially introduced into service in 1979. The helicopter was named after the Native American leader, Black Hawk, of the Sauk tribe.
The UH-60 was selected over its competitors mainly due to its superior performance and advanced technology. It was designed with the twin-turboshaft engine, better survivability, and improved cargo capabilities in mind. Over the years, the Black Hawk has been adapted into numerous variants for different roles, including search and rescue, medical evacuation, and special operations. It has been extensively used by the U.S. military and has also been exported to various other countries.
The UH-60 Black Hawk has a conventional layout with a twin-turboshaft engine that powers a four-bladed main rotor and a four-bladed tail rotor. The main rotor is fully articulated, improving its flight capabilities across various conditions. Its power typically comes from two General Electric T700 turboshaft engines, each generating between 1,600 to 2,000 shaft horsepower, depending on the variant. The helicopter features a monocoque fuselage, designed for increased durability and crashworthiness, using materials like composite and titanium to enhance survivability.
The cockpit is built for two pilots and comes equipped with modern avionics, such as multi-function displays, GPS navigation, and secure communications systems. The cabin is spacious enough to carry up to 11 fully equipped troops or different cargo configurations, including six stretchers in a MedEvac role. For improved aerodynamics during flight, the Black Hawk employs a retractable landing gear system consisting of two main wheels and a tailwheel.
Armament
The UH-60 Black Hawk was originally conceived as a utility and transport helicopter, but its design allows for various armament configurations based on mission requirements. It's important to note that the UH-60 itself is not typically a dedicated attack helicopter like the AH-64 Apache; however, it can be equipped with a range of weaponry for self-defense and limited assault missions. Here are some of the weapon options:
- Machine Guns: The most common armament is the fitting of 7.62 mm machine guns on either side of the aircraft. These can be M240 machine guns or similar models, mounted on pintle mounts at the helicopter's side windows or doorways.
- Rockets: Some configurations allow for the mounting of 2.75-inch (70 mm) Hydra 70 rocket pods, which can be used for ground attacks.
- Gatling Guns: Some special operations variants can be fitted with a GAU-19, a .50-caliber Gatling gun, for increased firepower.
- Hellfire Missiles: While not standard, some Black Hawks have been modified to carry AGM-114 Hellfire missiles, usually associated with dedicated attack helicopters.
- Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System (APKWS): This is a laser-guided rocket system that turns unguided rockets into precision-guided munitions. Some Black Hawks have been equipped to deploy APKWS.
Different U.S. military branches and other countries have modified the Black Hawk to various extents, creating specialized versions such as the MH-60 (special operations) that may feature more advanced armament options. Nonetheless, the primary role of the UH-60 remains troop transport and utility, and its weapon systems are generally intended to complement that role.
Operational history
The UH-60 Black Hawk has a long and extensive operational history, starting from its introduction into U.S. Army service in 1979. It has been used in a variety of roles and operations both domestically and internationally. Here are some key highlights:
- 1980s: The Black Hawk saw its first combat action in the invasion of Grenada in 1983, known as Operation Urgent Fury. It was also deployed in Panama during Operation Just Cause in 1989.
- Gulf War: During the 1990-1991 Gulf War, the UH-60 played a critical role in troop transport, MedEvac, and logistics support. It was heavily used in Operations Desert Shield and Desert Storm.
- Balkans: The Black Hawk participated in peacekeeping operations in the Balkans during the 1990s, particularly in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
- Afghanistan: Since 2001, the UH-60 has been a workhorse in the ongoing conflict in Afghanistan, employed in a range of roles from troop transport and supply to MedEvac and special operations missions.
- Iraq: The Black Hawk saw extensive service during the Iraq War starting in 2003, performing similar roles as in Afghanistan.
- Humanitarian Operations: Beyond combat, it has been involved in numerous humanitarian missions, including disaster relief efforts for earthquakes, hurricanes, and other natural disasters.
- Special Operations: Special variants like the MH-60 have been used in high-profile special operations missions, including the raid that killed Osama bin Laden in 2011.
Variants
- UH-60A: This is the original Army utility tactical transport helicopter, which was later updated to the UH-60L with more powerful engines and improved gearboxes.
- UH-60M: The latest standard U.S. Army version, featuring upgraded T700-GE-701D engines, improved rotor blades, and state-of-the-art electronic instrumentation.
- SH-60 Seahawk: Adapted for naval operations, this variant includes features such as anti-submarine warfare (ASW) and anti-surface warfare (ASuW) capabilities.
- MH-60 Black Hawk: Special operations variant used by the U.S. Army and Navy. This includes the MH-60K for the Army and MH-60R and MH-60S for the Navy. These are equipped with advanced avionics and can carry a wider array of weapons.
- HH-60 Pave Hawk: This is a search and rescue (SAR) and MedEvac version used by the U.S. Air Force. It includes additional fuel tanks for extended range and additional electronic equipment for its specific mission profile.
- VH-60N White Hawk: This is a VIP transport variant primarily used to transport the President of the United States and other dignitaries.
- S-70: This is the export or commercial variant of the UH-60, and it comes in several sub-variants tailored to the needs of foreign governments.
- HH-60G Pave Hawk: An Air Force variant focused on combat search and rescue (CSAR), it has additional fuel tanks, armament, and a hoist for extracting personnel.
- UH-60Q MedEvac: This version is specifically outfitted for medical evacuation roles, featuring medical equipment such as stretchers and life-support systems.
- LUH-72 Lakota: Though not a direct UH-60 variant, the Lakota is based on the UH-60's commercial counterpart and serves in utility roles, including MedEvac and logistics.
Technical specifications
| Version: UH-60L | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 2 pilots + 2 |
| Operational range | 593 km (368 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 294 km/h (183 mph) |
| Wingspan | 16.4 m (53.7 ft) |
| Height | 4.9 m (16.1 ft) |
| Length | 19.5 m (64.1 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 5,791 m (18,999 ft) |
| Empty weight | 4,819 kg (10,624 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 10,659 kg (23,499 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 3.6 m/s (11.8 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops General Electric T700-GE-701C delivering 1208 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
United States | 2827 (+321) | |
|
Japan | 214 (+24) | |

|
South Korea | 139 (+12) | |

|
Turkey | 90 (+45) | |

|
Saudi Arabia | 81 (+203) | |

|
United Arab Emirates | 80 | |

|
Colombia | 75 | |

|
Taiwan | 61 (+12) | |

|
Israel | 50 | |

|
Greece | 49 (+4) | |

|
Australia | 33 (+43) | |

|
Jordan | 31 (+2) | |

|
Brazil | 26 (+12) | |

|
Mexico | 24 (+7) | |

|
China | 23 | |
|
Thailand | 23 | |

|
Philippines | 20 (+27) | |

|
Spain | 18 (+8) | |

|
Brunei | 16 | |

|
Sweden | 15 (+12) | |

|
Austria | 9 (+12) | |

|
Denmark | 9 | |

|
Slovakia | 9 | |

|
Bahrain | 8 | |

|
Singapore | 8 | |

|
Tunisia | 8 | |
|
India | 6 (+18) | |
|
Poland | 6 (+2) | |

|
Chile | 6 | |
|
Croatia | 4 (+8) | |

|
Latvia | 3 (+1) | |

|
Afghanistan | 3 | |

|
Albania | 2 (+4) | |

|
Egypt | 2 | |
|
Indonesia | 0 (+24) | |
|
Lithuania | 0 (+6) | |

|
Norway | 0 (+6) | |
All operators
Armament
Missiles payload:
- Anti-Tank Lockheed-Martin AGM-114 Hellfire