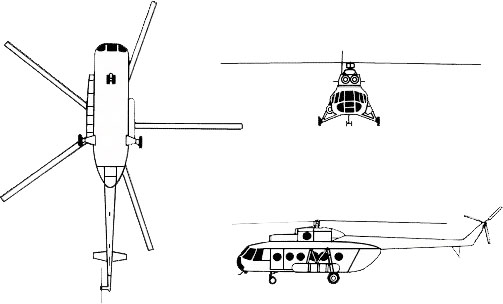
Mi-8 Hip
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇨🇳 Ex-USSR |
| Manufacturer | Mil |
| First flight | 24 June 1961 |
| Year introduced | 1967 |
| Number produced | 17000 units |
| Average unit price | $4 million |
Description
The Mi-8 Hip is a medium twin-turbine helicopter originally designed by the Soviet Union. It was produced by the Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant and first flew in 1961. The aircraft was developed as a response to the need for a more powerful and versatile helicopter, capable of fulfilling various roles ranging from transport to attack missions. The Mi-8 became one of the world's most-produced helicopters, with thousands in operation across various countries and configurations. It has been widely exported and serves in both military and civilian roles globally.
The Mi-8 Hip features a conventional helicopter design with a single five-blade main rotor and a three-blade tail rotor. It's powered by two turboshaft engines mounted on top of the fuselage, near the main rotor. The cockpit accommodates two pilots, and the spacious cabin is versatile, allowing for a variety of configurations to meet different mission requirements. Depending on its role, the Mi-8 can be outfitted with hardpoints for armaments, or it can be configured to carry troops, cargo, or medical supplies. The helicopter is also designed for all-weather, day-and-night operations, and has been updated with modern avionics systems in its more recent variants.
The aircraft's structure is largely composed of aluminum, and it is known for its robustness and reliability. The main rotor's five-blade design offers stability and lifting capability, which contribute to the Mi-8's utility in a range of scenarios, from high-altitude flights to humanitarian relief missions.
Armament
The Mi-8 Hip has a modular design that allows it to be equipped with various armaments depending on its intended role. In its armed configuration, often designated as Mi-8MT or Mi-17 for export, it can be outfitted with a variety of weapons. These can include machine guns mounted in the cabin windows or on pintle mounts, rocket pods, and anti-tank guided missiles. Commonly used machine guns are PKT 7.62mm or YakB-12.7mm, and rocket options often include the S-8 rocket pods.
For anti-armor roles, it can carry AT-2 Swatter or AT-3 Sagger anti-tank missiles. Some variants are even compatible with more advanced systems like the Igla or Strela surface-to-air missiles for limited air defense capability. It's worth noting that while the Mi-8 has these weapon capabilities, it's not optimized as an attack helicopter. Its armaments are generally considered secondary to its primary roles of transport and utility.
In terms of defensive measures, the Mi-8 can be equipped with countermeasures such as flare and chaff dispensers to disrupt incoming missiles. Some variants also feature armor plating for increased protection against small arms fire and anti-aircraft artillery.
Operational history
The Mi-8 has a long and diverse operational history that spans over six decades. Introduced in the early 1960s, it was quickly adopted by the Soviet Armed Forces and has since been used in various capacities by over 50 countries.
During the Cold War, the Mi-8 saw extensive service, especially within the Warsaw Pact nations. It played a significant role in Afghanistan during the Soviet-Afghan War from 1979 to 1989, where it was used for troop transport, supply runs, and casualty evacuation. It also served as a gunship, providing fire support to ground forces, but suffered significant losses due to the guerilla tactics of the mujahideen and the introduction of U.S.-supplied Stinger missiles.
In addition to its military roles, the Mi-8 has been actively used for civilian purposes, such as search and rescue, medical evacuation, and firefighting. It played a crucial role in disaster relief operations, including the aftermath of earthquakes, floods, and other natural disasters.
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the Mi-8 continued to see action in various regional conflicts. It was used in the Balkans during the Yugoslav Wars, the Chechen Wars in Russia, and more recently in the conflicts in Iraq, Syria, and Ukraine.
Variants
- Mi-8T: This is the basic transport variant, designed for carrying cargo or up to 24 troops. It can be armed with rockets and anti-tank guided missiles but is generally used in the utility role.
- Mi-8TV: Known as the Mi-17 when exported, this version is more combat-oriented. It features strengthened armor and improved weapon systems, including more hardpoints for armaments.
- Mi-8MT: Also known as Mi-17 in its export version, this is an improved version of the Mi-8TV, featuring more powerful engines and advanced avionics.
- Mi-8AMTSh: Also known as the Mi-171Sh, this is a modernized combat-transport version with more advanced avionics, night vision capability, and a variety of weapons options, including guided missiles.
- Mi-8VIP: These are luxury versions tailored for VIP transport. The interiors are usually customized and can include amenities like air conditioning, soundproofing, and entertainment systems.
- Mi-8PPA: This is an electronic warfare variant used for jamming enemy radar and communications.
- Mi-8MPS: This is a search-and-rescue (SAR) version, outfitted with specialized equipment for locating and retrieving personnel.
- Mi-8MTV: Designed for operations in high-altitude and hot-and-high conditions, this variant features more powerful engines and rotor improvements for better performance under these conditions.
- Mi-8AMT: This is a civil version commonly used for transporting passengers or cargo and can also be configured for roles like firefighting and medical evacuation.
- Mi-8MSB: An upgraded version done by Ukrainian firms, it features new engines and rotors, giving it improved performance and fuel efficiency.
Technical specifications
| Version: Mi-8T Hip-C | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 2 pilots + 1 flight engineer |
| Operational range | 425 km (264 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 250 km/h (155 mph) |
| Wingspan | 21.3 m (69.8 ft) |
| Height | 5.7 m (18.5 ft) |
| Length | 25.2 m (82.8 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 4,500 m (14,764 ft) |
| Empty weight | 7,160 kg (15,785 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 12,000 kg (26,455 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops Klimov TV2-117 delivering 1119 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
Russia | 789 (+10) | |

|
Algeria | 140 | |

|
Vietnam | 89 | |
|
Ukraine | 73 | |

|
Angola | 65 | |

|
Azerbaijan | 64 | |

|
Egypt | 62 | |
|
Pakistan | 50 | |

|
Kazakhstan | 49 | |
|
Syria | 49 | |

|
Peru | 44 | |

|
Iraq | 43 | |

|
North Korea | 41 | |

|
Uzbekistan | 39 | |
|
Poland | 38 | |

|
Belarus | 36 | |

|
Yemen | 34 | |

|
Sri Lanka | 27 | |

|
Mexico | 24 | |

|
Sudan | 24 | |

|
Georgia | 17 | |
|
Armenia | 16 | |

|
Ethiopia | 15 | |

|
Turkmenistan | 15 | |

|
Tajikistan | 14 | |

|
Myanmar | 13 | |

|
Serbia | 11 | |
|
Cambodia | 10 | |

|
Nicaragua | 10 | |
|
Thailand | 10 | |

|
United States | 10 | |

|
Cuba | 9 | |

|
Afghanistan | 8 | |

|
China | 8 | |
|
Libya | 7 | |
| 🇨🇩 | Congo Democratic Republic | 6 | |

|
Congo | 6 | |
|
North Macedonia | 6 | |

|
Chad | 6 | |
| 🇧🇦 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 5 | |

|
Hungary | 5 | |

|
Kyrgyzstan | 5 | |

|
Mozambique | 4 | |

|
Togo | 4 | |

|
Burkina Faso | 3 (+2) | |
| 🇧🇹 | Bhutan | 2 | |

|
Ivory Coast | 2 | |

|
Djibouti | 2 | |

|
Namibia | 2 | |

|
Colombia | 1 | |
|
Lithuania | 1 | |

|
Moldova | 1 | |
All operators