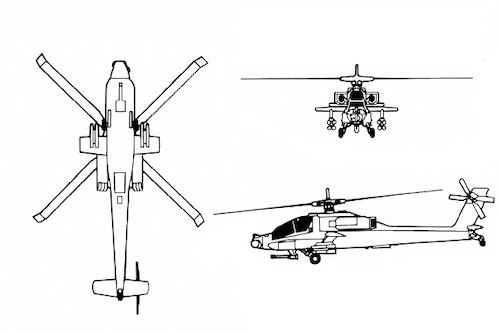
AH-64 Apache
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇺🇸 United States |
| Manufacturer | Boeing |
| First flight | 30 September 1975 |
| Year introduced | 1984 |
| Number produced | 2400 units |
| Average unit price | $33 million |
Description
The AH-64 Apache is an American twin-turboshaft attack helicopter developed by Hughes Helicopters for the United States Army. Its development began in the early 1970s to replace the AH-1 Cobra. The Apache was first flown on September 30, 1975, and was introduced into service in April 1986. It was later produced by McDonnell Douglas and is currently produced by Boeing. The primary mission of the AH-64 is as a highly advanced multi-role combat helicopter, designed for armed reconnaissance, close air support, and anti-tank warfare.
The AH-64 Apache features a tandem cockpit design, where the pilot sits behind and above the co-pilot/gunner. Both crew members are capable of flying the aircraft and performing methods of weapon engagements independently. The Apache is designed for survivability; it has a robust set of armor and redundant systems to improve battle resilience. It is powered by two General Electric T700 turboshaft engines, each providing up to 1,900 horsepower.
One of the helicopter's most distinguishing features is its integrated electronic warfare suite, which provides both passive and active means of detecting and countering threats. Its avionics package is also among the most advanced, allowing for significant flexibility in mission profiles. The aircraft is equipped with a nose-mounted sensor suite for target acquisition and night vision.
The Apache's rotor system allows for significant maneuverability, including the ability to perform rapid direction changes, climb, and hover in challenging conditions. This agility makes it well-suited for the kinds of low-level operations and "nap-of-the-earth" flying that are often required in modern conflicts.
Armament
The AH-64 Apache is heavily armed and built around its various weapon systems, tailored for anti-armor, anti-fortification, and close air support roles. Here are its main weapon capabilities:
- 30 mm M230 Chain Gun: Mounted under the fuselage and controlled by the co-pilot/gunner, this is the Apache's primary close-range weapon. It can fire high-explosive or armor-penetrating rounds at a rate of about 625 rounds per minute.
- AGM-114 Hellfire Missiles: These are laser-guided, air-to-surface missiles designed primarily for anti-armor roles. They have a range of up to 8 km and are capable of defeating most modern main battle tanks. Later versions of the Hellfire also offer "fire-and-forget" capabilities.
- Hydra 70 Rocket Pods: These unguided rockets are useful for softer targets like enemy infantry formations or light vehicles. They are often used in a suppression role, laying down fire over an area rather than targeting individual vehicles.
- AIM-9 Sidewinder: Some Apache models have the capability to carry air-to-air missiles like the AIM-9 Sidewinder for self-defense against enemy aircraft, though this is not a primary role for the Apache.
- Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System (APKWS): This is a guidance kit that turns existing Hydra 70 unguided rockets into precision-guided munitions, giving them similar accuracy to the Hellfire missiles but at a lower cost per shot.
- Stinger and Mistral Missiles: Some versions have the option to carry air-to-air missiles for defense against enemy helicopters and low-flying aircraft.
Operational history
The AH-64 Apache has an extensive operational history, having been deployed in various conflicts around the world since its introduction into service in 1986. Here are some key deployments:
- Gulf War (1990-1991): The AH-64 saw its first combat in Operation Desert Storm. The Apache's played a pivotal role in the destruction of Iraqi armor and fortifications. They were responsible for taking out radar installations and anti-aircraft systems in the opening phases of the conflict.
- Kosovo War (1999): Apaches were deployed as part of the NATO intervention but faced logistical and operational challenges. Two helicopters crashed during training exercises, and none saw combat, marking this as a somewhat controversial deployment for the Apache.
- Afghanistan (2001-present): The Apache has been used extensively in Operation Enduring Freedom for various mission profiles including close air support, armed reconnaissance, and anti-terrorism operations.
- Iraq War (2003-2011): The AH-64 was a workhorse in Operation Iraqi Freedom, providing close air support for ground troops and engaging in anti-armor operations against Iraqi forces. They were essential in urban combat scenarios, particularly during the battle for Fallujah.
- Israel: The Israeli Defense Forces have used their variant, the AH-64D Saraf, in various conflicts, including the Second Lebanon War (2006) and various operations in the Gaza Strip.
- Syria: AH-64s have been used to engage ISIS targets as part of the international coalition against the extremist group.
- Other Operations: Apaches have been involved in numerous other military operations and peacekeeping missions, including in Panama, Libya, and the Balkans. They've also been sold to various countries and have seen service in conflicts such as the Yemeni and Nagorno-Karabakh wars.
Variants
- AH-64A: The initial production model introduced in 1986. It was equipped with the T700-GE-701 engines and TV-guided AGM-114 Hellfire missiles.
- AH-64B: This was a proposed upgrade that was ultimately skipped in favor of moving directly to the AH-64D variant.
- AH-64D Apache Longbow: Introduced in the late 1990s, this is a significantly upgraded version featuring the Longbow fire-control radar, which allows it to fire Hellfire missiles at targets without having to expose itself to enemy fire. It also has updated avionics and more powerful T700-GE-701C engines.
- AH-64E Guardian: The latest variant, previously known as AH-64D Block III. It has more powerful T700-GE-701D engines, improved rotor blades for better lift, and enhanced avionics and systems that allow for better interaction with drones and other networked battlefield elements. It was introduced into service in 2011.
- AH-64D Saraf: Customized for the Israeli Air Force, the Saraf includes unique avionic systems made by Israeli firms, as well as compatibility with Israeli-made air-to-surface munitions.
- WAH-64 Apache: A British variant manufactured under license by AgustaWestland (now Leonardo). It is similar to the AH-64D but features Rolls-Royce engines and some other unique equipment suited to the requirements of the British Army.
- AH-64DJP Apache: A version tailored for the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force, built under license in Japan.
- AH-64I: An Indian variant that incorporates specific Indian systems and avionics, developed as part of a deal for 22 Apaches signed in 2015.
- AH-64E V6: A specific version of the AH-64E with maritime capabilities, such as the ability to operate more effectively over water and in naval scenarios.
Technical specifications
| Version: AH-64D Apache Longbow | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 1 pilot + 1 WSO |
| Operational range | 485 km (301 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 265 km/h (165 mph) |
| Wingspan | 14.6 m (48.0 ft) |
| Height | 5.0 m (16.2 ft) |
| Length | 17.7 m (58.2 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 5,670 m (18,602 ft) |
| Empty weight | 5,352 kg (11,799 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 10,107 kg (22,282 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 15.7 m/s (51.5 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops General Electric T700-GE-701C delivering 1208 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
United States | 824 (+15) | |

|
Israel | 48 | |

|
Egypt | 46 | |
|
United Kingdom | 37 (+13) | |

|
South Korea | 36 (+36) | |

|
Saudi Arabia | 34 (+49) | |

|
United Arab Emirates | 30 (+39) | |

|
Greece | 29 | |

|
Taiwan | 29 | |
|
Qatar | 24 (+24) | |
|
India | 22 (+12) | |

|
Singapore | 18 | |

|
Kuwait | 16 (+8) | |

|
Netherlands | 12 (+16) | |
|
Japan | 12 | |
|
Indonesia | 8 | |
|
Poland | 0 (+96) | |

|
Morocco | 0 (+36) | |

|
Australia | 0 (+29) | |
All operators
Armament
Missiles payload:
- Anti-Tank Lockheed-Martin AGM-114 Hellfire
- Air-to-Air Short-Range Raytheon AIM-9 Sidewinder