H145M / EC645
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇫🇷 France |
| Manufacturer | Airbus Helicopters |
| First flight | 12 June 1999 |
| Year introduced | 2002 |
| Number produced | 1500 units |
| Average unit price | $25 million |
Technical specifications
| Version: UH-72A | |
|---|---|
| Operational range | 660 km (410 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 269 km/h (167 mph) |
| Wingspan | 10.8 m (35.4 ft) |
| Height | 3.5 m (11.3 ft) |
| Length | 13.0 m (42.7 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 5,486 m (17,999 ft) |
| Empty weight | 1,792 kg (3,951 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 3,585 kg (7,904 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 8.13 m/s (26.7 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops Turbomeca Arriel 1E2 delivering 550 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
United States | 483 (+30) | |

|
Germany | 24 (+80) | |

|
Hungary | 19 | |
|
Thailand | 16 (+3) | |
|
United Kingdom | 10 (+3) | |

|
Serbia | 8 (+7) | |

|
Kazakhstan | 8 | |

|
South Africa | 8 | |

|
Ecuador | 6 | |
|
Indonesia | 4 | |

|
Bolivia | 3 | |

|
Belgium | 0 (+15) | |
All operators


Description
The EC145's origins stem from a joint development effort between Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm, later Eurocopter, and Kawasaki Heavy Industries, building upon their successful BK 117 C1 collaboration. Rather than a new design, the EC145 integrated the forward cockpit and avionics of Eurocopter's EC135 with the BK 117's rear section. Originally designated as BK 117 C2, the design sought to improve upon its predecessor with greater range, payload, cabin size, reduced noise and vibration, and simplified maintenance. Type-certificated as the BK 117 C2, the helicopter was selected by the French Defense and Civil Guard in December 1997 for air rescue missions. The first EC145 flew on 12 June 1999 in Donauwörth, Germany. Safety certification was granted by German, Japanese, and US aviation authorities between December 2000 and January 2002. Eurocopter and Kawasaki agreed to independently manufacture and market the helicopter while collaborating on development and upgrades, extending their partnership until at least 2025.
The EC145 features a cabin space larger than its BK 117 C1 predecessor. The design incorporates composite rotor blades derived from the EC135, contributing to an increased maximum take-off weight and greater range. Its hingeless rotor system utilizes a monolithic titanium hub, and it is powered by two Turboméca Arriel turboshaft engines, with later models employing the Arriel 2E. A variable rotorspeed and torque matching system (VARTOMS) is integrated to manage rotor performance and noise signature. The cockpit includes a Thales Avionics MEGHAS Flight Control Display System with active matrix liquid crystal displays. Many systems feature independent redundancy, including the autopilot, hydraulic boost, transmission lubrication, and certain sensors. The EC145 T2 includes a full 4-axis autopilot, dual-channel Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC), and three large LCD primary displays.
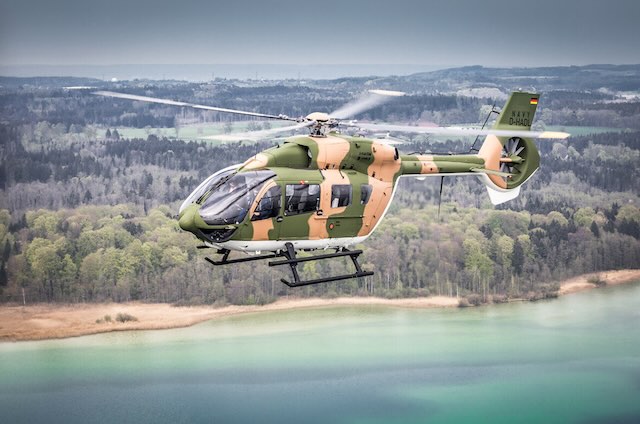
The H145M, a militarized variant, can be outfitted with equipment for military operations, including ballistic protection and self-sealing fuel tanks. The helicopter can also be equipped with an electro-optical/infrared sensor for reconnaissance and targeting, along with retractable pintle-mounted 7.62 mm FN MAG machine guns or M134 miniguns. Military-grade communication and navigation systems are integrated, alongside an electronic warfare self-protection system. The H145M's HForce weapon system facilitates aiming of 12.7 mm and 20 mm gun pods, as well as 70 mm guided and unguided rockets. An anti-armor capability can be integrated via the SPIKE ER2 missile.
The H145 family has seen extensive operational use across civilian and military roles. The French Sécurité Civile, French Gendarmerie, and the Landespolizei of Hesse, Germany were early users. These early deployments involved air rescue and law enforcement missions. Military variants, such as the UH-72 Lakota in the United States Army, have been used for training, logistics, medical evacuation, and disaster response. Germany purchased 15 EC145s for special operations. The armed EC645 T2, equipped with weapon mounts, electronic countermeasures, and ballistic protection, serves in specialized roles. The H145M has been adopted by countries including Thailand, Serbia, and Hungary, utilizing the HForce weapon system for light attack and troop transport.
Main Variants:
-
EC145: The basic model derived from the BK 117 C-1, powered by Turbomeca Arriel 1E2 turboshaft engines and featuring a conventional high boom tail rotor.
-
ACH145: A corporate version offered by Airbus Corporate Helicopters with customizable interior and airframe options across two product lines.
-
EC145e: A utility-focused variant of the base EC145, incorporating a Garmin G500H digital cockpit and reduced weight achieved by system removal and a standardized interior.
-
H145: This updated version, initially designated EC145 T2, features a fenestron tail rotor, Arriel 2E engines, and advanced avionics, with a later variant introducing a five-blade bearingless main rotor system.
-
H145M: The militarized version of the H145, previously EC645 T2, equipped with ballistic protection, self-sealing fuel tanks, and the HForce weapon system for precision targeting with various armaments.