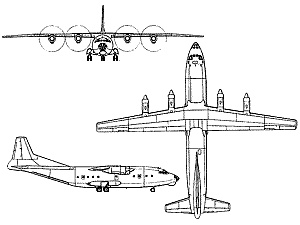
An-12 Cub
Summary
| Category | Military Transport Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇺🇦 Ukraine |
| Manufacturer | Antonov |
| First flight | 16 December 1957 |
| Year introduced | 1959 |
| Number produced | 1248 units |
| Average unit price | $8 million |
Description
Developed from the Antonov An-8, the An-12 was conceived as the military counterpart to the An-10 passenger transport. The first prototype of the An-12 first flew in December 1957, subsequently entering Soviet military service in 1959. Initially, production was centered at the State Aviation Factory in Irkutsk, Siberia. In 1962, manufacturing relocated to Tashkent, where approximately 830 were assembled. Production was later expanded to Voronezh and Kazan. The aircraft remained in production in the USSR until 1973.
The An-12 was specifically designed as a military transport aircraft. It features a rear loading ramp/door, enabling the transport of up to 100 fully equipped paratroopers or 20,000 kg (44,000 lb) of cargo. In military use, it can also transport up to two BMD-1 armored vehicles. Soviet military and former-Soviet An-12s were equipped with a defensive tail gun turret housing two 23 mm Nudelman-Rikhter NR-23 cannons.
The An-12 became extensively operated by the Soviet Air Forces and those of its allies. It saw use during the Soviet-Afghan War, associated with transporting the remains of fallen soldiers back to Tashkent, earning the nickname "Black Tulip." Beyond the Soviet Union, the An-12 was widely exported and operated by numerous air forces across the globe. The Indian Air Force, for instance, inducted the An-12 in 1961 and employed it in roles including airlifting reinforcements during the Sino-Indian War of 1962 and as a heavy bomber during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971. The An-12 has been largely retired from Russian and Ukrainian service, but continues to serve with air forces in countries such as Angola, Sudan and Myanmar.
Main Variants:
-
An-12BP: The upgraded variant with increased take-off weights and additional fuel capacity, which became the standard tactical transport of the Soviet and other air forces.
-
Y-8: The Chinese version of the An-12, reverse-engineered and produced locally after the Sino-Soviet split, incorporating a Tu-16/H-6 bomber navigator cockpit design instead of the original An-12's shorter cockpit.
-
Y8-F600: A joint venture between Shaanxi Aircraft Company, Antonov ASTC, and Pratt & Whitney Canada, featuring a redesigned fuselage, western avionics, and PW150B turboprop engines.
Technical specifications
| Version: An-12BP Cub-A | |
|---|---|
| Maximum speed | 770 km/h (478 mph) |
| Wing area | 121.7 m² (1310.3 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 38 m (124.7 ft) |
| Height | 10.5 m (34.5 ft) |
| Length | 33.1 m (108.6 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 10,200 m (33,465 ft) |
| Empty weight | 28,000 kg (61,729 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 61,000 kg (134,482 lbs) |
| Takeoff distance | 900 m (2,953 ft) |
| Powerplant | 4 x turboprops Ivchenko-Progress AI-20M delivering 3126 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
China | 194 | |

|
Russia | 64 | |

|
Angola | 8 | |

|
Venezuela | 8 | |

|
Myanmar | 5 (+1) | |

|
Sudan | 5 | |

|
Ethiopia | 4 | |
|
Pakistan | 4 | |
|
Libya | 3 | |

|
Tanzania | 2 | |

|
Uzbekistan | 2 | |

|
Sri Lanka | 1 | |
All operators