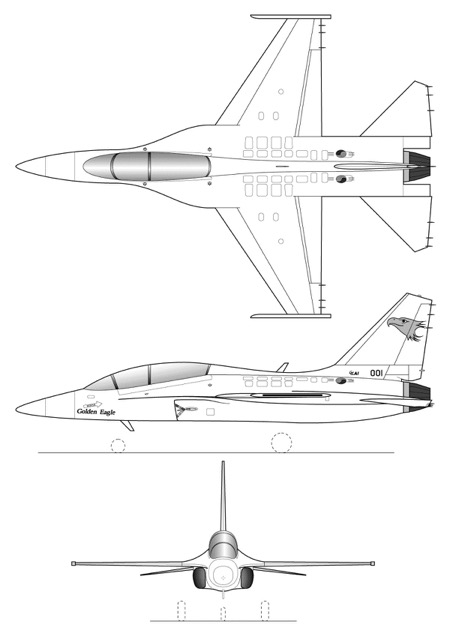
T-50 Golden Eagle
Summary
| Category | Military Training Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇰🇷 South Korea |
| Manufacturer | KAI |
| First flight | 20 August 2002 |
| Year introduced | 2005 |
| Number produced | 200 units |
| Average unit price | $43 million |
Description
The T-50 Golden Eagle is a family of South Korean supersonic advanced trainers and light combat aircraft. Developed by Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) in partnership with Lockheed Martin, the T-50 was conceived in the late 1990s to replace the aging fleet of trainer aircraft used by the Republic of Korea Air Force (ROKAF). It made its first flight on August 20, 2002. The development aimed to produce an aircraft capable of both training new pilots and performing light combat missions, effectively serving a dual role. It was also designed with export in mind, targeting the global market for trainer and light attack aircraft.
The development of the T-50 Golden Eagle was a substantial undertaking that involved collaboration between Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) and Lockheed Martin. With an initial focus on meeting the needs of the Republic of Korea Air Force (ROKAF), the developers aimed to create an aircraft that could not only serve as an advanced trainer but also perform light combat roles, thereby achieving a versatile multi-role capability.
The design was influenced by Lockheed Martin's extensive experience in fighter aircraft, notably drawing on some technologies from the F-16 Fighting Falcon. The aircraft features a single-engine layout with a digital fly-by-wire control system, providing high maneuverability and ease of control. The cockpit is equipped with a glass panel, incorporating a hands-on-throttle-and-stick (HOTAS) control system to minimize pilot workload. The T-50 also boasts advanced avionics, including multi-mode radar and a modern electronic warfare suite, which contribute to its light combat capabilities.
Another notable feature is its aerodynamic design. The aircraft employs a leading-edge root extension (LERX), which allows for better agility and control at various speed ranges.
Armament
The T-50 Golden Eagle is equipped to carry a variety of weapons, making it more than just a training aircraft—it has light combat capabilities as well. The aircraft comes with a single internal General Dynamics 20mm rotary cannon and has provisions for carrying external armaments.
In terms of external ordnance, the T-50 has seven hardpoints: one under the fuselage and three under each wing. These hardpoints are capable of carrying a range of munitions, including air-to-air missiles such as the AIM-9 Sidewinder, air-to-surface missiles like the AGM-65 Maverick, and various types of precision-guided bombs. It can also carry rocket pods and external fuel tanks to extend its range or endurance.
The aircraft's avionics suite is equipped to handle these weapons systems efficiently. Its multi-mode radar allows for effective targeting, and the advanced fire-control system is designed to manage various types of munitions.
The T-50's light combat variant, often referred to as the FA-50, expands upon these capabilities. The FA-50 is equipped with more advanced radar and avionics, allowing it to handle a wider range of weapons and systems. This variant is intended for multirole missions and has a more robust air-to-ground as well as air-to-air combat capability compared to the basic T-50 trainer variant.
Operational history
The T-50 Golden Eagle entered service with the Republic of Korea Air Force (ROKAF) in 2005 as an advanced trainer. Its combat variant, the FA-50, became operational in 2013. The aircraft has been primarily used for pilot training, but the FA-50 variant has also seen operational deployments, notably serving in air-to-ground and air-to-air roles for the ROKAF.
Internationally, the T-50 has been exported to several countries. Indonesia became the first foreign customer, acquiring a variant called the T-50i for its Air Force. The Philippines also purchased the FA-50PH light fighter variant, deploying them for various roles including air-to-air and air-to-ground missions. Iraq has also acquired the T-50IQ variant, using it primarily for training, but with the capability for combat roles. In addition to these countries, Thailand and Turkmenistan have also purchased variants of the T-50.
The aircraft gained some combat experience when the Philippine Air Force deployed FA-50PHs against Islamist militants during the 2017 Battle of Marawi. The FA-50PHs were used in air-to-ground roles, deploying munitions against enemy positions, proving their operational effectiveness in combat situations.
Variants
- T-50A: This is the basic trainer variant, designed primarily for pilot training. It lacks the advanced avionics and weapon systems found in the combat versions but retains high maneuverability and performance suitable for training roles.
- T-50B: This variant is designed for aerobatic performances and is used by the ROKAF's aerobatic team, the Black Eagles. It shares many similarities with the T-50A but includes smoke generators and specialized avionics for aerobatic displays.
- TA-50: This is a light attack variant equipped with a radar and an internal 20mm cannon. It has the ability to carry a variety of air-to-air and air-to-ground munitions. It serves as an intermediate step between the basic T-50A trainer and the more advanced FA-50 combat variant.
- FA-50: This is the most combat-capable version, designed for multirole missions. It features advanced radar, avionics, and increased internal fuel storage. The FA-50 is capable of air-to-air, air-to-ground, and reconnaissance missions.
- T-50i: Customized for the Indonesian Air Force, this variant is primarily intended for training but retains some light attack capabilities.
- FA-50PH: This is a variant purchased by the Philippine Air Force, which is similar to the standard FA-50 but may include specific customizations to meet the needs of the Philippine military.
- T-50IQ: Specifically tailored for the Iraqi Air Force, this variant focuses on training but also has light attack capabilities, similar to the TA-50.
Technical specifications
| Version: T-50 | |
|---|---|
| Operational range | 1,851 km (1,150 mi) |
| Wingspan | 9.2 m (30.1 ft) |
| Height | 4.8 m (15.7 ft) |
| Length | 13.0 m (42.6 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 16,764 m (55,000 ft) |
| Empty weight | 6,441 kg (14,200 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 13,472 kg (29,701 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 1 x turbojet General Electric F404-GE-102 delivering 5409 kgf each |
Further Reading Ad
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
South Korea | 145 (+17) | |

|
Iraq | 24 | |
|
Thailand | 14 | |
|
Poland | 12 (+36) | |

|
Philippines | 12 | |

|
Malaysia | 0 (+36) | |
All operators