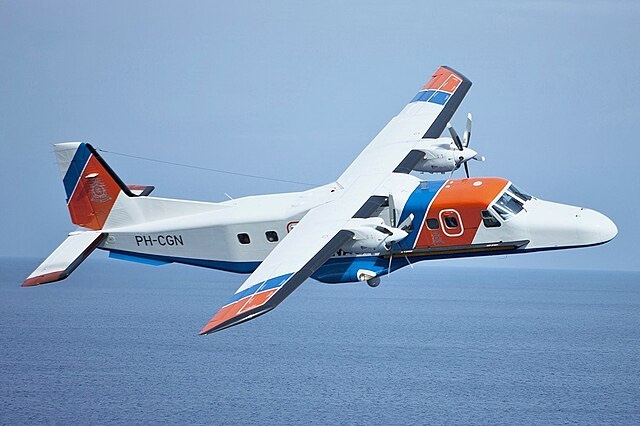
Do 228
Summary
| Category | Military Transport Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇩🇪 Germany |
| Manufacturer | Dornier |
| First flight | 28 March 1981 |
| Year introduced | 1982 |
| Number produced | 370 units |
| Average unit price | $8 million |
Description
In the late 1970s, Dornier GmbH embarked on developing a new wing design, the TNT (Tragflügel neuer Technologie), supported by the German Government. After testing it on a modified Do 28D-2 Skyservant, the company designed a new fuselage for the TNT and TPE 331–5 engines, creating two variants, a 15-passenger and a 19-passenger version, designated E-1 (later Dornier 228-100) and E-2 (later Dornier 228-200), respectively. The new aircraft was presented to the public at the ILA Berlin Air Show in 1980, and the two prototypes made their first flights on 28 March 1981 and 9 May 1981. Following German certification on 18 December 1981, the Dornier 228-100 entered service with Norving in July 1982, with the Dornier 228-200 entering service with Jet Charters later the same year. By 1983, Dornier was producing three aircraft per month. A license-production and technology-transfer agreement was signed with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) in November 1983, establishing a separate production line that produced its first aircraft in 1985. In 1998, German production was halted to concentrate on other programs and address wider financial difficulties.
The Dornier 228 is a twin-engine general purpose aircraft designed to carry up to 19 passengers or various cargoes. It is powered by two Garrett TPE331 turboprop engines and is classified as a Short Takeoff and Landing (STOL) aircraft, capable of operating from rough runways and in hot climates, largely attributed to its supercritical wing, which generates significant lift at slow speeds. The rectangular shape of the fuselage and large side-loading doors make it particularly suitable for utility operations.
The wing structure consists of a box formed from four integrally-milled alloy panels, with Kevlar used for the ribs, stringers, trailing edge, and fowler flaps, leading to a 15% reduction in weight, elimination of 12,000 rivets, and a decrease in manufacturing workload.
Both the fuselage and tail are of conventional design, utilizing chemical milling for weight reduction.
The aircraft can be configured as a commuter, military transporter, cargo hauler, or special missions aircraft, with optional equipment including surveillance radar, FLIR, search lights, and operator stations. A VIP cabin configuration is also available, and air conditioning is standard.
The Dornier 228NG features over 350 design changes, including a Universal UNS-1 glass cockpit, new five-blade fibre-composite propellers, and optimized Garrett TPE331-10 engines.
The Dornier 228 has been promoted for various special missions, including maritime surveillance, border patrol, medevac, search and rescue, paradrop, and environmental research. Special equipment available to be installed include a 360-degree surveillance radar, side-looking airborne radar, forward-looking infrared (FLIR) sensor, search light, operator station, real-time datalink, enlarged fuel tanks, satellite uplink, stretches, air-openable roller door, and infrared/ultraviolet sensors.
The Dornier 228 has seen operational use in various roles across the globe. The aircraft's versatility has allowed it to serve as a commuter aircraft, military transporter, cargo hauler, and special missions platform. Its ability to operate from rough runways and in hot climates, combined with a long flight endurance, has made it suitable for maritime surveillance, border patrol, medevac, search and rescue, paradrop, and environmental research missions. The Dornier 228 is operated by airlines, police, law enforcement, paramilitary, and military organizations. By July 2018, the global fleet had accumulated over four million flight hours.
Main Variants:
-
Dornier 228-100: The initial production variant, designed for 15 passengers.
-
Dornier 228-200: A larger variant of the Dornier 228, designed for 19 passengers.
-
Dornier 228NG: A modernized version with a new five-blade propeller, more powerful engines, and an advanced glass cockpit.
-
Hindustan 228: A licensed version manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) in India, modified for commercial operations.
-
Hybrid-electric demonstrator: A modified Dornier 228 used by the German DLR to test hybrid-electric propulsion systems.
Technical specifications
| Version: Do 228-212 | |
|---|---|
| Maximum speed | 433 km/h (269 mph) |
| Wing area | 32 m² (344.4 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 17.0 m (55.7 ft) |
| Height | 4.9 m (15.9 ft) |
| Length | 16.6 m (54.3 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 8,534 m (27,999 ft) |
| Empty weight | 3,739 kg (8,243 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 6,400 kg (14,110 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 7.5 m/s (24.6 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops Garrett TPE331-5-252D delivering 578 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
India | 90 (+6) | |

|
Nigeria | 7 | |
|
Thailand | 7 | |
|
Bangladesh | 4 | |
|
Italy | 3 | |

|
Venezuela | 3 | |

|
Germany | 2 | |
| 🇲🇻 | Maldives | 2 | |

|
Malawi | 2 | |

|
Seychelles | 1 (+2) | |

|
Niger | 1 | |
All operators
