AW139
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom • 🇮🇹 Italy |
| Manufacturer | AgustaWestland |
| First flight | 3 February 2001 |
| Year introduced | 2003 |
| Number produced | 1100 units |
| Average unit price | $15 million |
Description
In 1997, Agusta launched a program to develop a replacement for the Bell Huey family of helicopters. In 1998, Bell and Agusta formed a joint venture, Bell/Agusta Aerospace Company (BAAC), to develop both a conventional helicopter and a tiltrotor aircraft, designated the Bell/Agusta AB139 and Bell/Agusta BA609, respectively. Agusta took the lead on the AB139's development. Bristow Helicopters placed the first order in September 2000. The first preproduction helicopter flew on 3 February 2001 at Vergiate, Italy. The first production AW139 made its first flight on 24 June 2002. European JAA certification was received in June 2003, with FAA type certification following in December 2004. By May 2005, over 100 orders had been placed. In 2005, AgustaWestland acquired Bell's 25% share in the program for $95 million. In April 2008, AgustaWestland announced an increase in the AW139's max gross weight to 14,991 lb (6,800 kg). A second production line was established at the United States AgustaWestland Aerospace plant in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 2007.
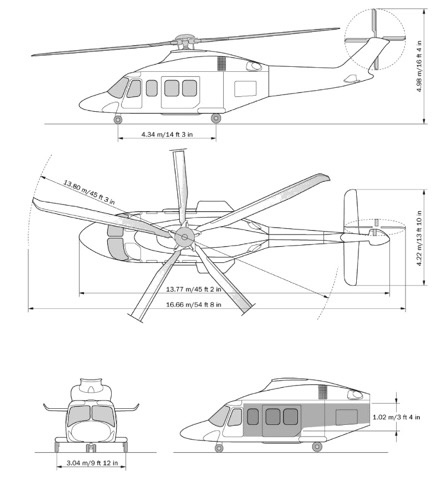
The AW139 is a conventional twin-engine multi-role helicopter featuring a five-bladed fully articulated main rotor with a titanium hub and composite blades, complemented by a four-bladed articulated tail rotor. It is equipped with retractable tricycle landing gear, where the two aft wheels retract into external sponsons that also accommodate emergency equipment. The cockpit incorporates the modular Honeywell Primus EPIC avionics system with a four LCD screen glass cockpit and is designed for a crew of two pilots, though most aircraft include a four-axis autopilot which facilitates single-pilot operations under instrument flight rules (SPIFR) and enables advanced functions such as auto-hover. The cockpit can also be modified for night vision goggle compatibility. The aircraft can accommodate up to 15 passengers in three rows of five. Furthermore, the AW139 can be configured with over a thousand customizable equipment options, including auxiliary fuel tanks, rescue hoists, cargo hooks, search and weather radar, ice protection systems, external cameras, and searchlights.
The AW139M, a militarized variant of the AW139, is capable of carrying various weapons payloads via an external stores system. The AW139M's design incorporates several features tailored for military operations, including a high definition forward-looking infrared (FLIR) system and self-protection systems. Options offered include armored seats, self-sealing fuel tanks, and a full ice protection system for all-weather operations.
The AW139 has seen widespread operational use. The Irish Air Corps was the first military operator, receiving their initial batch in 2006. Other early military adopters included the air forces of the United Arab Emirates and Qatar. The AW139M, a dedicated militarized variant, was procured by the Italian Air Force and designated HH-139A for combat search and rescue missions. In Japan, the Coast Guard adopted the AW139 as a replacement for its Bell 212 fleet for search and rescue, with the National Police Agency also procuring the type. Civilian operators such as CHC Helicopter have utilized the AW139 extensively in search and rescue, emergency medical service, and offshore transport roles, becoming the largest global operator of the type in 2012. In 2018, the United States Air Force selected the MH-139 Grey Wolf, an AW139 variant, to replace its aging UH-1N fleet.
Main Variants:
-
AB139: This is the original Italian-built production aircraft, with 54 units produced.
-
AW139: This designation applies from the 55th aircraft onwards, built in Italy, marking a continuation of the production line.
-
AW139 (long nose configuration): This variant features an extended nose to provide increased space for avionics equipment, and is manufactured in both Italy and the United States.
-
AW139M: A militarized version of the AW139, it is designed for military operations and capable of carrying external payloads.
-
MH-139A Grey Wolf: Developed by Boeing in partnership with Leonardo, this military variant was selected by the United States Air Force.
Technical specifications
| Version: AW139 | |
|---|---|
| Maximum speed | 310 km/h (193 mph) |
| Height | 3.7 m (12.2 ft) |
| Length | 13.8 m (45.2 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 6,096 m (20,000 ft) |
| Empty weight | 3,622 kg (7,985 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 6,400 kg (14,110 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 10.9 m/s (35.8 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6C-67C delivering 1141 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Italy | 33 | |
|
Pakistan | 19 | |
|
Qatar | 19 | |

|
Algeria | 14 | |

|
United Arab Emirates | 12 | |

|
United States | 8 (+74) | |
|
Thailand | 8 | |

|
Ireland | 6 | |

|
Panama | 6 | |

|
Angola | 4 | |
|
Bangladesh | 4 | |

|
Egypt | 4 | |

|
Cyprus | 3 | |

|
Kenya | 3 | |

|
Malta | 3 | |

|
Malaysia | 2 | |

|
Nigeria | 2 | |

|
Gabon | 1 | |
|
Indonesia | 1 | |
|
Libya | 1 | |

|
Nepal | 1 | |

|
Turkmenistan | 0 (+8) | |

|
Slovenia | 0 (+6) | |
All operators