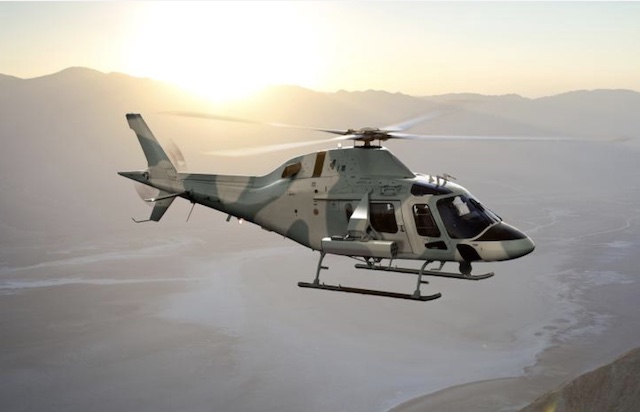
AW119
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom • 🇮🇹 Italy |
| Manufacturer | AgustaWestland |
| First flight | 1 February 1995 |
| Year introduced | 2000 |
| Number produced | 300 units |
| Average unit price | $3.1 million |
Description
The A119 Koala helicopter was conceived in 1994, with the first prototype being used for static tests. The second prototype's first flight took place in February 1995. Original certification was targeted for 1997, but this timeline was not met due to factors including personnel resource allocation to the A109 Power program and requirements for further development to satisfy customer expectations. To address performance requirements, the planned Turboméca Arriel 2K1 turboshafts were replaced by the Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6B engine. By 1998, the prototypes were remanufactured with this engine and assigned new serial numbers, leading to certification in December 1999 and FAA approval in February 2000. Customer deliveries commenced subsequently, with the initial commercial example delivered to Linfox, an Australian logistics company. The AW119Ke (Koala Enhanced) was introduced in April 2007 at Heli-Expo, featuring modified rotor blades, increased rotor rpm, higher payload capacity, enhanced hot-and-high performance, and improved cabin versatility. Fuselages for the AW119 are produced by PZL-Świdnik in Poland, a subsidiary of AgustaWestland. Final assembly was initially conducted in Vergiate, Italy, and later transferred to AgustaWestland's facility in Philadelphia, United States, concurrent with the start of AW119Ke production.
The AW119 is a single-engine multirole helicopter developed from the Agusta A109. Key distinguishing features include its single Pratt & Whitney PT6B-37A turboshaft engine and fixed skids, in contrast to the twin-engine configuration and retractable wheeled landing gear of the A109. It utilizes the same cockpit and cabin as the A109. The rotorcraft is equipped with a four-bladed fully articulated main rotor system utilizing composite blades designed for optimal lift and reduced noise signature, incorporating tip caps and requiring no lubrication for its elastomeric bearings. The airframe incorporates aluminum honeycomb structural panels for noise and vibration attenuation. The AW119 is configured to accommodate up to seven passengers in a three-abreast seating arrangement. For emergency medical service (EMS) missions, it can carry up to two stretchers along with medical personnel. A selection of avionics is available, including the Garmin G1000 glass cockpit in the AW119Kx variant, which enhances situational awareness and mitigates pilot workload. Primary flight data is displayed on two 10.4-inch multi-function displays, complemented by a stand-by display. Optional equipment includes an external hoist, cargo hook, snow skis, and a forward-looking infrared (FLIR) camera. Fuel tanks enable a flight endurance approaching six hours. The AW119 holds a sling load capacity of up to 1,400 kg (3,086 lb).
While primarily designed for civil operations, the AW119 can be configured for law enforcement roles. In these configurations, it can carry specialized equipment such as searchlights, loudspeakers, and forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras. A rappelling kit can also be installed for tactical personnel deployment.
Since 2009, efforts have been undertaken to establish local assembly of the AW119 in India. In 2014, a legal challenge was filed against the United States Army's procurement of the Eurocopter UH-72 Lakota as a trainer aircraft, arguing the AW119 presented lower costs; this challenge was dismissed. The AW119 has been proposed as a replacement for the US Navy's Bell TH-57 trainer helicopters, leading to the development of the TH-119 variant, later designated TH-73A and named "Thrasher". The US Navy anticipates acquiring up to 130 units of the TH-73A. Several air forces and law enforcement agencies worldwide operate the AW119, including the Algerian Air Force, Bangladesh Air Force, Ecuadorian Air Force, Finnish Border Guard, Israeli Air Force, Portuguese Air Force, Turkish Land Forces, New York City Police Department, and United States Navy.
Main Variants:
-
A119: The original production version of the helicopter, with a maximum take-off weight of 2,720 kg (5,997 lb).
-
AW119 MkII: An improved version featuring redesigned rotors, a greater payload capacity, and better fuel efficiency.
-
AW119 Ke: A marketing designation for the AW119 MkII (Koala Enhanced).
-
AW119 Kx: The successor to the Ke model, equipped with the Garmin G1000H avionic suite and produced in Philadelphia, USA and Hyderabad, India.
-
TH-73A Thrasher: A military training variant developed for the US Navy.
Technical specifications
| Version: AW119Kx | |
|---|---|
| Height | 3.6 m (11.8 ft) |
| Length | 12.9 m (42.4 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 4,572 m (15,000 ft) |
| Empty weight | 1,483 kg (3,269 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 2,850 kg (6,283 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 9.4 m/s (30.8 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 1 x turboprop Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6B-37A delivering 747 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
United States | 100 (+30) | |

|
Algeria | 8 | |

|
Portugal | 7 | |

|
Turkey | 4 (+8) | |

|
Ecuador | 4 | |
|
Bangladesh | 2 | |

|
Israel | 1 (+12) | |
All operators
Armament
Missiles payload:
- Anti-Tank BGM-71 TOW
- Air-to-Air Short-Range General Dynamics AIM-92 Stinger
- Anti-Tank HOT
- Anti-Tank Lockheed-Martin AGM-114 Hellfire
- Air-to-Air Short-Range Mistral
