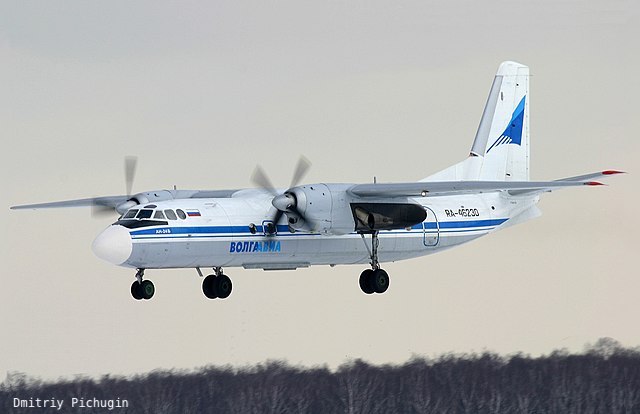
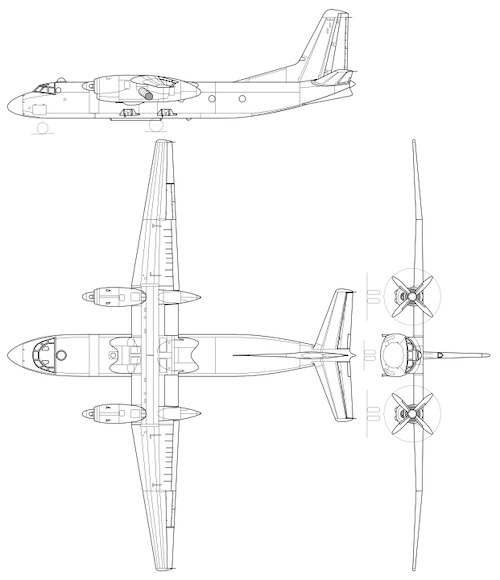
An-24 Coke
Summary
| Category | Military Transport Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇺🇦 Ukraine |
| Manufacturer | Antonov |
| First flight | 20 October 1959 |
| Year introduced | 1962 |
| Number produced | 1367 units |
| Average unit price | $8 million |
Description
Designed in 1957 by the Antonov Design Bureau in the Soviet Union, the An-24 was a 44-seat twin turboprop transport/passenger aircraft intended to replace the Ilyushin Il-14 on short to medium haul routes. Optimized for operations from rough strips and unprepared airports in remote areas, the An-24's high-wing layout was chosen to protect the engines and blades from debris. Its rugged design required minimal ground support equipment, while the aircraft's high power-to-weight ratio offered enhanced performance. First flown in 1959, the An-24 was manufactured by the Kyiv, Irkutsk and Ulan-Ude Aviation Factories, with production ceasing in the USSR by 1978. The Kyiv-Svyatoshino plant (later renamed "Aviant") constructed 985 examples, Ulan Ude built 180, and Irkutsk produced 197 An-24T tactical transport/freighters. Total production amounted to approximately 1,000 units.
The An-24 was conceived to replace the Ilyushin Il-14 on short to medium haul routes, specifically optimized for operation from rough airstrips and unprepared airports in remote locations; the high-wing layout protects the engines and blades from debris. Its rugged airframe allowed for adaptation to secondary roles such as ice reconnaissance and as an engine/propeller testbed, while further development led to the An-26 tactical transport, An-30 photo-mapping/survey aircraft and An-32 tactical transport featuring more powerful engines. Several variants of the An-24 exist, each with specific modifications for different roles, such as the An-24T tactical transport equipped with a ventral loading hatch, cargo winch, and escape hatch, or the An-24RT, similar to the An-24T but fitted with an auxiliary turbojet engine. Special mission aircraft included the An-24LR 'Toros' for ice reconnaissance, equipped with SLAR (sideways looking airborne radar) and the An-24RR for Nuclear, biological and chemical warfare reconnaissance versions, carrying air sampling pods and a sensor pod. Search and rescue (SAR) modifications (An-24PRT) included rescue equipment and exploration devices.
The An-24 was not designed as a combat aircraft and is not typically armed. Certain specialized military variants, such as the An-24T tactical transport, featured a ventral loading hatch and cargo winch for transporting troops and supplies, but were not equipped with offensive weaponry. Reconnaissance or surveillance roles (An-24RR) involved modifications with radar and sensor pods but did not include adding offensive weapons capabilities.
The An-24 has seen widespread use across various theaters, primarily within the Soviet Union and among its satellite states, as well as in Africa. As a rugged and reliable aircraft, it was well-suited for operations from rough strips and unprepared airports in remote locations. The An-24 also served in military roles, including tactical transport, with specialized variants developed for search and rescue, ice reconnaissance, and airborne command post duties. Its operational strengths included a high power-to-weight ratio, a design that protected engines from debris, and minimal ground support requirements. The aircraft was eventually proposed for accelerated decommissioning following fatal incidents, leading to a ban on scheduled flights inside Russia, although it continues to see limited commercial service. Beyond its initial Soviet operators, the An-24 was adopted by numerous air forces globally, including those of Cambodia, North Korea, Syria, and Ukraine.
Main Variants:
-
An-24: The initial production model, separate from the prototypes, entering service in 1962 and later exported to Cuba for use as military transports.
-
An-24A: An improved version seating 44 passengers with a larger interior volume and the APU exhaust moved to the tip of the starboard nacelle, with 200 aircraft built.
-
An-24B: The second production version with seating for up to 52 passengers, an increased maximum takeoff weight, additional windows, and modifications to the flaps, with 400 aircraft built.
-
An-24T (Transportnyy – transport): A tactical transport aircraft equipped with a ventral loading hatch, cargo winch, and escape hatch for transporting airborne troops and infantry.
-
An-24V: An export version of the An-24B, equipped with an AI-24T turboprop engine, available in early and late models, with variations in wing design, flaps, and interior configuration for cargo or passenger transport.
Technical specifications
| Version: An-24B | |
|---|---|
| Wing area | 75.0 m² (807.0 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 29.2 m (95.8 ft) |
| Height | 8.3 m (27.3 ft) |
| Length | 23.5 m (77.2 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 8,400 m (27,559 ft) |
| Empty weight | 13,300 kg (29,321 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops Ivchenko-Progress AI-24A delivering 1876 kW each |
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|

|
China | 91 | |

|
Russia | 24 | |
|
Ukraine | 22 | |

|
Kazakhstan | 7 | |

|
Cuba | 4 | |

|
Yemen | 3 | |

|
North Korea | 1 | |
All operators