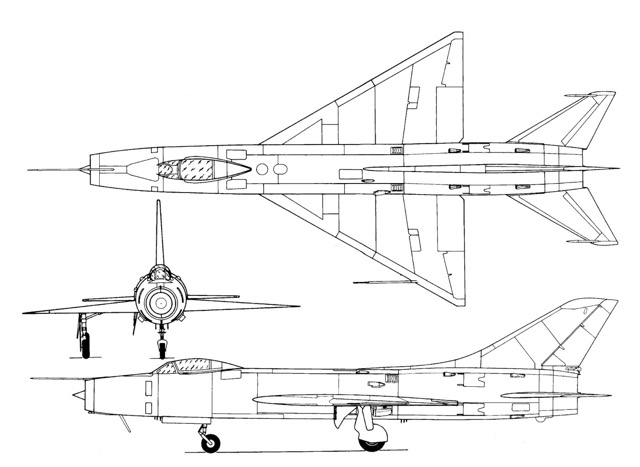
Su-9 / Su-11 Fishpot
Summary
| Category | Combat Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇨🇳 Ex-USSR |
| Manufacturer | Sukhoi |
| First flight | 20 June 1958 |
| Year introduced | 1959 |
| Number produced | 1150 units |
| Average unit price | $5 million |
Description
The Su-9's development stemmed from aerodynamic studies conducted by TsAGI during the Korean War, which explored optimal aerodynamic configurations for jet fighters. The aircraft first took to the skies as the T-405 prototype in 1956. Developed concurrently with the Su-7 "Fitter," both aircraft were unveiled to the West at the Tushino Aviation Day on June 24, 1956, where the Su-9 was initially misidentified as Fitter-B. Entering service in 1959, the Su-9 marked a significant step in Soviet interceptor design. Total production reached approximately 1,100 aircraft. By the 1970s, remaining Su-9s and Su-11s were retired, with some repurposed as test vehicles or converted into unmanned aerial vehicles. The Su-9 was superseded by the improved Su-11 and the more advanced Su-15 "Flagon" and MiG-25 "Foxbat" interceptors.
The Su-9's design incorporated a fuselage and tail surfaces reminiscent of the Su-7, yet distinguished itself with a 53° delta wing, offering lower drag at supersonic speeds, and conventional slab tailplanes. Retaining Sukhoi's signature rear-fuselage air brakes and the Su-7's Lyulka AL-7 turbojet engine with a nose intake, the Su-9 housed its R1L radar set within its translating shock cone. Its delta wing facilitated a modest increase in fuel capacity compared to the Su-7.
The Su-9 was primarily armed with four K-5 (AA-1 "Alkali") beam-riding air-to-air missiles. It carried no cannon armament. There were two fuselage pylons reserved for the carriage of drop tanks. In addition to these, the aircraft featured four under-wing hardpoints, allowing it to carry up to 500 kg (1,100 lb) of disposable stores in various combinations.
The Su-9 served primarily within the Soviet Anti-Air Defense forces, with no exports to client states or Warsaw Pact nations. Tasked with routine patrols and interdictions over Soviet frontiers, its most notable operational event was the attempted interception of Francis Gary Powers' U-2 spy plane on May 1, 1960, though the Su-9 was unarmed and unable to effectively engage due to the speed disparity, and ultimately did not cause the U-2's destruction. As the Su-9 was phased out, Bobrovka became the Soviet Union's primary storage facility, with at least 243 Su-9 aircraft observed parked there by 1981.
Main Variants:
-
T-405: This was the prototype model that served as the basis for the Su-9's development.
-
Su-9: The primary production variant, with approximately 1,100 units manufactured and deployed.
-
Su-9U: This was a two-seat training version equipped with a full avionics suite but lacking weapon systems or hardpoints.
-
T-431: A specially modified Su-9 variant was created to set a world record for absolute height in 1962.
-
Sukhoi Su-11: This was an upgraded design based on the Su-9, featuring a slightly lengthened fuselage but was ultimately superseded by the Su-15.
Technical specifications
| Version: Su-9 / Su-11 Fishpot | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 1 pilot |
| Maximum speed | 2135 km/h (1327 mph) |
| Wing area | 26.3 m² (282.6 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 8.4 m (27.7 ft) |
| Length | 16.7 m (54.8 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 16,800 m (55,118 ft) |
| Empty weight | 8,750 kg (19,290 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 1 x Lyulka AL-7F delivering 9060 kgf each |
Current operating countries
All operators