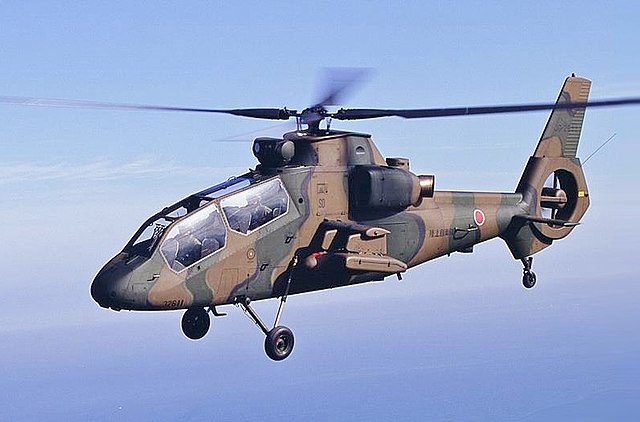
OH-1 Ninja
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇯🇵 Japan |
| Manufacturer | Kawasaki |
| First flight | 6 August 1996 |
| Year introduced | 2000 |
| Number produced | 38 units |
Description
During the late 1980s, the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force (JGSDF) initiated the OH-X program to find a replacement for its Kawasaki-built OH-6D scout/observation helicopters. Kawasaki's proposal was selected in 1991, leading to formal development starting in October 1992, with Kawasaki responsible for 50 percent of the airframe and coordinating the rotor system's development. The first OH-1 prototype, designated XOH-1, was rolled out in early 1996 and conducted its maiden flight on August 6, 1996. Four prototypes were flight tested until 1998, accumulating 400 hours. Manufacturing of production OH-1s commenced in June 1998, following an initial order for two units. The JGSDF originally planned to procure between 150 and 250 OH-Xs, and production proceeded slowly, with only a few units procured each year.
The OH-1 Light Observation Helicopter features a tandem-seat configuration and is powered by two turboshaft engines. Its narrow fuselage incorporates small stub wings and a non-retractable tailwheel undercarriage. Equipped with an automatic pilot system that includes flight holding, the cockpit utilizes a multi-display system. Power is provided by a pair of Mitsubishi TS1 turboshaft engines with Full Authority Digital Engine Controls (FADEC), driving a four-blade composite main rotor with a bearingless rotor hub and a Fenestron-type anti-torque tail rotor. For surveillance, it mounts a roof-mounted electro-optical sensor turret forward of the rotor head, incorporating a forward-looking infrared sensor, a laser rangefinder, and a color TV camera. Four hardpoints beneath the stub wings provide a total capacity of 132 kg (291 lb) for external stores. The outer pylons are designed to carry up to four Type 91 air-to-air missiles. The inner pylons accommodate external fuel tanks.
The Kawasaki OH-1 entered service with the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force (JGSDF) in January 2000. As of March 2014, a total of 38 OH-1s had been commissioned. In December 2022, the Japanese government announced plans to retire 33 OH-1s along with other aircraft in favor of unmanned aerial vehicles, reflecting a shift towards efficient defense spending.
Main Variants:
-
XOH-1: This was the prototype version of the OH-1, serving as the initial design and test platform for the production model.
-
OH-1: This is the production model, which is primarily used as an observation helicopter by the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force.
-
AH-2: This was a proposed attack helicopter derivative, intended to have uprated engines and additional anti-tank armaments, but was ultimately rejected in favor of the Boeing AH-64 Apache.
Technical specifications
| Version: OH-1 | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 2 members |
| Operational range | 550 km (342 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 278 km/h (173 mph) |
| Height | 3.8 m (12.5 ft) |
| Length | 12 m (39.4 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 4,880 m (16,010 ft) |
| Empty weight | 2,450 kg (5,401 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 4,000 kg (8,818 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turboprops Mitsubishi TS1-M-10 delivering 664 kW each |
Further Reading
As an Amazon Associate, we may earn from qualifying purchases.
Current operating countries
| Country | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Japan | 36 | |
All operators

