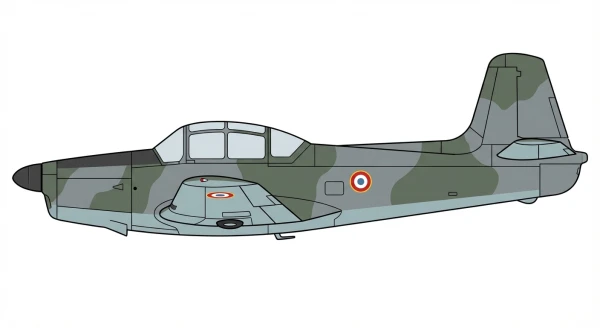
MS 733 Alcyon
Summary
| Category | Military Training Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇫🇷 France |
| Manufacturer | Morane-Saulnier |
| First flight | 11 August 1949 |
| Year introduced | 1953 |
| Number produced | 208 units |
| Average unit price | $0.2 million |
Description
Designed as a basic trainer for the French military, the prototype MS.730 first flew on 11 August 1949. This prototype was a low-wing cantilever monoplane featuring a fixed tailwheel landing gear and powered by a 180 hp (130 kW) Mathis 8G.20 inverted V8 engine. The engine was later replaced with a war-surplus 240 hp (180 kW) Argus As 10, and the modified prototype flew again in November 1949 as the MS.731. Following this, two further prototypes, designated MS.732, were built and flown in 1951. These were powered by a 200 hp Salmson 8.AS.02 engine, and the original fixed landing gear was replaced with retractable main wheels.
The production version that followed was designated the MS.733. The MS.733 was a low-wing cantilever monoplane and retained the retractable landing gear introduced on the MS.732 prototypes. It was equipped with full IFR equipment, including two VOR-ILS sets, one ADF set, two VHF radios, a radar altimeter, an attitude indicator, and a directional gyroscope, making it suitable for navigation training. The Alcyon proved to be a trainer facilitating basic aerobatic maneuvers and often replacing vintage Stampe SV.4 biplanes. Several civilian flying schools, including Air France, also utilized the Alcyon.
Some MS.733 aircraft were modified into MS.733A gunnery trainers, specifically adapted for counter-insurgency operations. These variants were equipped with a SFOM 83 reflector sight and two 7.5mm MAC 1934/M39 machine guns installed within the wings, each holding 500 rounds. Additionally, these models featured two under-wing hardpoints designed to carry munitions. A typical loadout included paired Matra Type 14 rocket rails, each capable of holding four SERAM 28 kg (62 lb) T10 heavy rockets in a 2x2 stacked configuration, along with a smaller hardpoint between the rocket rails rated for a 50 kg (110 lb) bomb. Standard MS.733 training models were not equipped with either machine guns or hardpoints. The MS.733A served from 1955 to 1959, before its replacement by the T-28S Fennec.
The production version, designated the MS.733, saw deployment across various French military branches and abroad. The French Navy received 40 aircraft, while the French Air Force acquired 145, with 70 of the latter equipped with machine guns for gunnery training. Some of these were later converted into MS.733A variants for counter-insurgency operations in Algeria. Post-war, some aircraft were sold to Morocco, and 15 aircraft were supplied to Cambodia.
Main Variants:
-
MS.730: The initial prototype was powered by a 180 hp Mathis 8G.20 engine, serving as the foundation for subsequent developments.
-
MS.731: This variant featured a re-engining of the initial prototype with a 240 hp Argus As 10 engine, marking an early modification in the aircraft's development.
-
MS.732: Two prototypes were built with a 200 hp Salmson 8.AS.02 engine and retractable landing gear.
-
MS.733: As the primary production model, it was equipped with a 240 hp Potez 6D 02 engine, with 205 aircraft manufactured in total.
-
MS.733A: This was a modified MS.733 gunnery trainer, adapted for counter-insurgency roles with machine guns and under-wing hardpoints.
Technical specifications
| Version: MS.733 | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 1 pilot + 1 instructor + 1 passenger |
| Operational range | 920 km (572 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 240 km/h (149 mph) |
| Wing area | 20.4 m² (219.6 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 11.3 m (37.0 ft) |
| Height | 3.5 m (11.4 ft) |
| Length | 9.3 m (30.6 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 4,800 m (15,748 ft) |
| Empty weight | 1,262 kg (2,782 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 1,670 kg (3,682 lbs) |
| Powerplant | 1 x pistons engine Potez 6D30 delivering 177 kW each |
Current operating countries