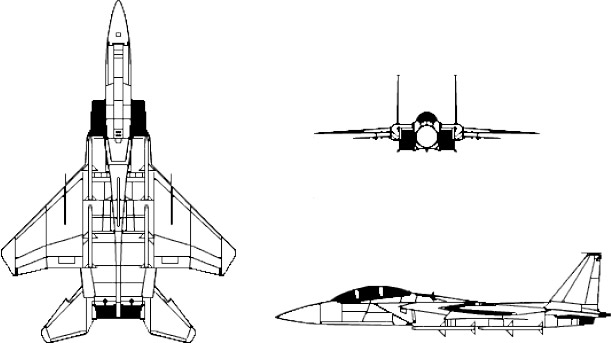
F-15 Eagle
Summary
| Category | Combat Aircraft |
| Origin country | 🇺🇸 United States |
| Manufacturer | McDonnell Douglas |
| First flight | 27 July 1972 |
| Year introduced | 1976 |
| Number produced | 1198 units |
| Average unit price | $29 million |
Description
The F-15's development originated in the early Vietnam War, driven by a mandate for common tactical aircraft. Initial studies in 1965 for a dedicated air superiority fighter, designated "F-X", emphasized maneuverability and speed, with a secondary ground-attack role. An official requirements document was released to 13 companies on 8 December 1965. Studies of air combat over Vietnam indicated that reliance on long-range missiles and optimized aircraft for that role placed larger U.S. aircraft at a disadvantage against smaller, less expensive day fighters like the MiG-21. This contributed to the development of energy–maneuverability theory. The emergence of the Soviet MiG-25 interceptor in 1967 accelerated the F-X program. A request for proposals issued in September 1968 called for a single-seat fighter with a maximum takeoff weight of 40,000 pounds (18,000 kg), a maximum speed of Mach 2.5, and a thrust-to-weight ratio approaching 1:1. Four companies submitted proposals, and McDonnell Douglas was selected on 23 December 1969. Formally named the "Eagle", initial versions included the single-seat F-15 and twin-seat TF-15, later standardized as F-15A and F-15B respectively. The first F-15A flight occurred on 27 July 1972, followed by the F-15B in July 1973.
The F-15 features an all-metal semi-monocoque fuselage and a large-cantilever, shoulder-mounted wing with a leading-edge sweepback angle of 45°. The trailing edge incorporates ailerons and a simple high-lift flap. The empennage, constructed from metal and composite materials, consists of twin aluminum alloy/composite honeycomb vertical stabilizers. Composite horizontal all-moving tails, positioned outboard of the vertical stabilizers, provide roll control in specific flight maneuvers. The aircraft is powered by two Pratt & Whitney F100 axial flow turbofan engines with afterburners, mounted side by side in the fuselage and supplied by rectangular inlets with variable intake ramps. The cockpit, situated high in the forward fuselage, features a one-piece windscreen and a large canopy providing extensive visibility. The airframe structural weight composition includes 37.3% aluminum, 29.2% honeycomb material, 25.8% titanium, 5.5% steel, and 2% composites and fiberglass. Starting in the 1980s, the structure incorporated advanced superplastically formed titanium components.
Its multimission avionics system comprises a head-up display (HUD), advanced radar, AN/ASN-109 inertial guidance system, flight instrumentation, ultra high frequency communications, tactical air navigation system, instrument landing system receivers, and an internally mounted tactical electronic warfare system.
The aircraft employs a versatile array of air-to-air weaponry, managed by an automated release system. Visual guidance information is displayed on the head-up display. The Eagle can carry combinations of up to four different air-to-air missiles: AIM-7F/M Sparrow or AIM-120 AMRAAM missiles on the lower fuselage corners, and AIM-9L/M Sidewinder or AIM-120 AMRAAM missiles on two pylons under the wings. An internal 20 mm (0.79 in) M61 Vulcan Gatling gun is mounted in the right wing root. For extended range, low-drag conformal fuel tanks (CFTs) can be attached to the sides of the engine air intakes. While not jettisonable in flight, CFTs allow all external munitions stations to remain available, including Sparrow or AMRAAM missile attachments on their corners.
The F-15 served as the primary air superiority fighter for the USAF and allied nations during the later stages of the Cold War, succeeding the F-4 Phantom II in this role. Its initial combat deployment was with the Israeli Air Force (IAF) in 1979. It saw significant action in the 1982 Lebanon War, during which Israeli F-15s were credited with destroying 41 Syrian aircraft in air-to-air combat. In USAF service, the aircraft participated in combat operations including Operation Urgent Fury, where it provided air cover in Grenada, and the 1991 Gulf War. During the Gulf War, USAF F-15s achieved 36 of the 39 air-to-air victories attributed to U.S. Air Force assets against Iraqi forces. The aircraft has since been deployed in support of Operation Southern Watch, patrolling Iraqi no-fly zones; Operation Provide Comfort in Turkey; NATO operations in Bosnia; and subsequent air expeditionary force deployments. The USAF began replacing its F-15A/B/C/D air superiority variants with the F-22 Raptor in the 2000s. The Eagle remains in service with numerous international operators.
Main Variants:
-
F-15A: The initial single-seat, all-weather air-superiority fighter version, with 384 aircraft built between 1972 and 1979.
-
F-15B: A two-seat training variant, originally designated TF-15A, with 61 aircraft built between 1972 and 1979, which is also fully combat-capable.
-
F-15C: An improved single-seat, all-weather air-superiority fighter version, with 483 aircraft built from 1979–1985, some of which were later upgraded with advanced radar systems.
-
F-15D: The two-seat training version of the F-15C, with 92 aircraft manufactured between 1979 and 1985, and utilized by the Israeli Air Force as a strike fighter.
-
F-15J: A single-seat all-weather air-superiority fighter for the Japan Air Self-Defense Force, with 139 built under license in Japan by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries from 1981–1997.
Technical specifications
| Version: F-15C | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 1 pilot |
| Operational range | 1,965 km (1,221 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 2655 km/h (1650 mph) |
| Wing area | 56.5 m² (608.2 sqft) |
| Wingspan | 13.1 m (42.8 ft) |
| Height | 5.6 m (18.5 ft) |
| Length | 19.4 m (63.7 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 19,812 m (65,000 ft) |
| Empty weight | 12,701 kg (28,001 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 30,844 kg (67,999 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 254.0 m/s (833.3 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 2 x turbojets Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-220 delivering 7915 kgf each |
| Ejection seat | McDonnell Douglas ACES II |
Current operating countries
All operators
Armament
Missiles payload:
- Air-to-Air Medium-Range AIM-7 Sparrow
- Air-to-Air Medium-Range AIM-120 AMRAAM
- Air-to-Air Short-Range Raytheon AIM-9 Sidewinder