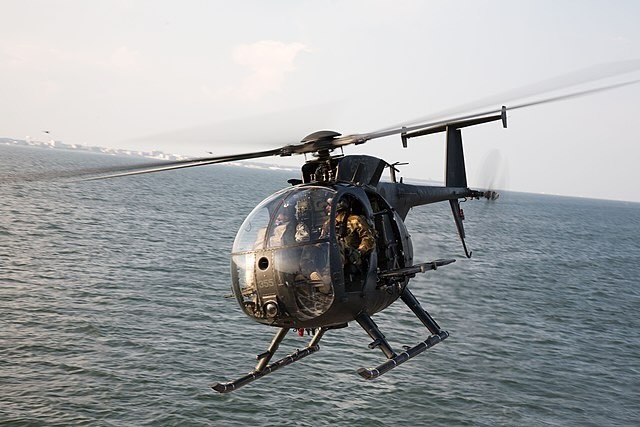
AH-6 Little Bird
Summary
| Category | Military Helicopters |
| Origin country | 🇺🇸 United States |
| Manufacturer | Boeing |
| First flight | 27 February 1963 |
| Year introduced | 1980 |
| Number produced | 1420 units |
| Average unit price | $7.5 million |
Description
The Boeing AH-6 series of light helicopter gunships evolved from the MH-6 Little Bird and MD 500 family. The program includes the Unmanned Little Bird (ULB) demonstrator, the A/MH-6X Mission Enhanced Little Bird (MELB), and the AH-6I and AH-6S variants. The ULB demonstrator, built from a civilian MD 530F, achieved its first flight on September 8, 2004, and its initial autonomous flight on October 16, 2004. The ULB was used to demonstrate the ability of an AH-64 Apache to remotely control the ULB's weapons payload as part of Boeing's Airborne Manned/Unmanned System Technology Demonstration (AMUST-D) program. Technologies from the ULB were incorporated into an A/MH-6, designated the A/MH-6X, which first flew on September 20, 2006. In 2009, the AH-6i, the export version of the AH-6S, first flew on September 16, 2009.
The AH-6 series design evolves from the MD 500 family. The Unmanned Little Bird (ULB) demonstrator features technologies for unmanned operation, including autonomous flight and remote weapons control from another helicopter via tactical common data link equipment. The ULB demonstrator has a payload capacity of 2,400 pounds (1,090 kg). The A/MH-6X Mission Enhanced Little Bird (MELB) expands on this with an additional 1,000 pounds of payload capacity, a prototype glass cockpit, and upgraded electronics and avionics. The proposed AH-6S Phoenix design includes a 15-inch stretch to accommodate downed crew recovery and an extended aerodynamic nose for avionics, incorporating AH-64D Block III composite blades and a more powerful Rolls-Royce 250-CE30 engine.
The AH-6 series can be fitted with 2× 12.7 mm (.50 cal) GAU-19 guns, or 2× 7.62 mm (.30 cal) M134 Miniguns. For ground targets, it can carry 2× LAU-68D/A seven-tube rocket pods for 2.75 in (70 mm) Hydra 70 rocket projectiles. Anti-tank capabilities are provided by 2× AGM-114 Hellfire missiles. For self-defense, the aircraft can be armed with 2× FIM-92 Stinger anti-air missiles.
The AH-6 family has been considered or procured by international air forces. Saudi Arabia requested 36 AH-6i aircraft with related equipment and weaponry through a Foreign Military Sale. Jordan has expressed interest in acquiring the AH-6i. The Royal Thai Army has ordered eight AH-6 aircraft.
Main Variants:
-
Unmanned Little Bird (ULB): This UAV demonstrator served as a testbed for autonomous flight and remote weapons control technologies.
-
A/MH-6X Mission Enhanced Little Bird (MELB): A hybrid of the ULB demonstrator and the A/MH-6M, featuring a prototype glass cockpit and upgraded electronics, with optionally manned or unmanned operation.
-
AH-6I: This is an export version of the AH-6S, tailored for international customers seeking advanced light attack helicopter capabilities.
-
AH-6S Phoenix: A proposed version for the US Army's Armed Aerial Scout program, stretched to accommodate additional personnel and equipped with advanced avionics.
Technical specifications
| Version: OH-6A Cayuse | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 2 members |
| Maximum speed | 282 km/h (175 mph) |
| Height | 2.6 m (8.6 ft) |
| Length | 9.2 m (30.1 ft) |
| Service ceiling | 4,877 m (16,001 ft) |
| Empty weight | 896 kg (1,975 lbs) |
| Max. takeoff weight | 1,610 kg (3,549 lbs) |
| Climb rate | 10.5 m/s (34.4 ft/s) |
| Powerplant | 1 x turboprop Allison T63-A5-A delivering 239 kW each |
All operators