United Arab Emirates Air Force
Key facts
| Official Name | United Arab Emirates Air Force |
| Local Name | القوات الجوية والدفاع الجوي الإماراتية (Al Quwwāt al Jawwīyah wal Difāʿ al Jawwī al Imārātīyah) |
| Country | 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates |
| World rank | #21 |
| Active aircraft | 551 as of 2026 |
| Aircraft on order | 261 |
| Roundel |
|
Overview
The United Arab Emirates Air Force (UAEAF) is a technologically advanced and combat-experienced force, structured to project power and defend national interests. Its organization is divided into the Western and Central Air Commands, headquartered in Abu Dhabi and Dubai respectively, alongside a Joint Aviation Command for rotary-wing assets. This structure allows for integrated command and control across its main operating bases, such as Al Dhafra and Al Minhad.
The UAEAF's strategic doctrine emphasizes maintaining a qualitative military edge through the acquisition of advanced Western hardware and developing interoperability with key partners like the United States and France. This doctrine is geared towards deterrence, primarily against Iran, and enables an expeditionary capability to conduct operations beyond its borders. This is reflected in a force structure built around multi-role combat aircraft capable of precision strike, air superiority, and reconnaissance missions. A focus on jointness aims to integrate air, land, and sea assets for combined arms effectiveness.
Recent engagements have demonstrated the UAEAF's operational capabilities. In Yemen, as part of the Saudi-led coalition, the Air Force provided close air support and strike capabilities, utilizing its F-16 and Mirage 2000 fleets. It also established forward operating bases to support these operations effectively. In Libya, the UAEAF conducted air operations, including drone strikes, in support of allied factions, showcasing its ability to sustain expeditionary campaigns far from its home territory. These campaigns have provided the UAEAF with significant combat experience.
The most notable recent acquisition is on 80 Dassault Rafale F4 fighters, a 4.5-generation aircraft that will form the future backbone of the force. This deal diversifies the UAE's combat fleet and provides advanced capabilities in electronic warfare and stand-off munitions. The UAE has also shown interest in 5th-generation technology, although a deal to acquire the F-35 from the US has stalled. Partnerships with countries like South Korea on future fighter projects indicate a long-term strategy to maintain technological superiority and reduce dependency on a single supplier.
Origin countries of aircraft
| Country | Active Aircraft | |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 United States | 322 | |
| 🇫🇷 France | 97 | |
| 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 56 | |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 24 | |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 22 | |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 20 | |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 14 | |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 9 | |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 9 | |
| 🇪🇺 Europe | 4 | |
| 🇨🇳 China | 2 | |
| 🇳🇿 New Zealand | 1 | |
| 🇹🇷 Turkey | 0 | |
Evolution of Emirati Air Force fleet
Aircraft by type in 2026
| Aircraft type | Active | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
247 | |
|
|
151 | |
|
|
86 | |
|
|
64 | |
|
|
3 | |
Full inventory in 2026
United Arab Emirates Air Force
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-16E |  |
🇺🇸 | 1979 | 55 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Mirage 2000-9/EAD/RAD |  |
🇫🇷 | 1983 | 44 | 0 |
0 |
||
| F-16F |  |
🇺🇸 | 1979 | 21 | 0 |
0 |
||
| AT-802 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1991 | 16 | -2 |
0 |
||
| Mirage 2000-9DAD |  |
🇫🇷 | 1983 | 15 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Rafale |  |
🇫🇷 | 2001 | 0 | 0 |
80 |
||
| F-35A |  |
🇺🇸 | 2013 | 0 | 0 |
50 |
||
| B-250 |  |
🇹🇷 | 2018 | 0 | 0 |
40 |
||
| Bell 407 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1967 | 14 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Bell 505 |  |
🇺🇸 | 2017 | 12 | 0 |
2 |
||
| AW139 |  |
🇬🇧 🇮🇹 | 2003 | 8 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Bell 412 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1959 | 4 | 0 |
0 |
||
| H125M/AS350/550 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1990 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| H125M/AS350 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1990 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
||
| C295/CN235 |  |
🇪🇸 🇮🇩 | 2001 | 9 | 0 |
0 |
||
| C-130H/L-100 | 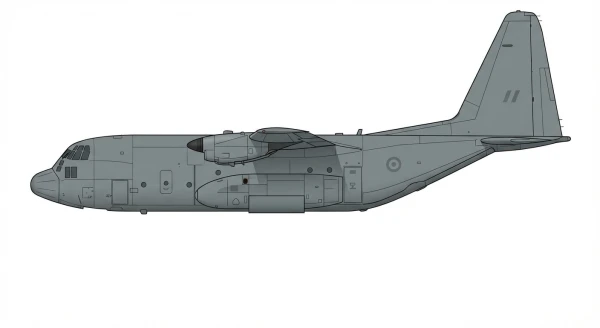 |
🇺🇸 | 1956 | 8 | 0 |
0 |
||
| C-17 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1993 | 8 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Global 6000 |  |
🇨🇦 | 1999 | 7 | +2 |
0 |
||
| A330 MRTT |  |
🇪🇺 | 1994 | 4 | +1 |
1 |
||
| Challenger 650 |  |
🇨🇦 | 1980 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| DHC-6 |  |
🇨🇦 | 1966 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Kodiak 100 |  |
🇺🇸 | 2008 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
||
| P-750 |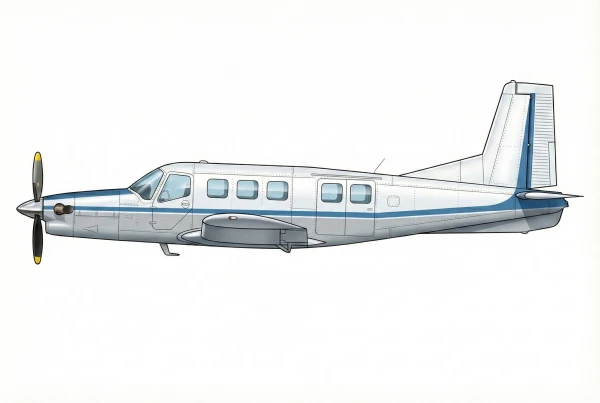  |
🇳🇿 | 2001 | 1 | 0 |
0 |
||
| PC-7 |  |
🇨🇭 | 1978 | 31 | 0 |
0 |
||
| PC-21 |  |
🇨🇭 | 2008 | 25 | 0 |
0 |
||
| G115 |  |
🇩🇪 | 1999 | 12 | 0 |
0 |
||
| Hawk 102 |  |
🇬🇧 | 1976 | 12 | 0 |
0 |
||
| L-15 |  |
🇨🇳 | 2013 | 2 | +2 |
46 |
||
| Dash 8 | 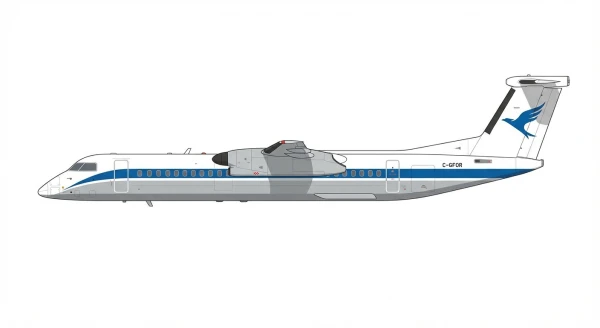 |
🇨🇦 | 1984 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| P180 |  |
🇮🇹 | 1990 | 2 | 0 |
0 |
||
| King Air 90 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1964 | 3 | 0 |
0 |
United Arab Emirates Joint Air Command
| Aircraft Type | Model | Origin Country | Model Year | Active | 𝚫 YoY | Ordered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-70/UH-60L/M |  |
🇺🇸 | 1979 | 80 | 0 |
0 |
||
| AH-64D/E |  |
🇺🇸 | 1984 | 30 | 0 |
39 |
||
| Bell 407 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1967 | 29 | 0 |
0 |
||
| CH-47C+/F |  |
🇺🇸 | 1962 | 28 | 0 |
0 |
||
| H125M/AS350/550 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1990 | 15 | 0 |
0 |
||
| AS565 |  |
🇫🇷 | 1990 | 12 | 0 |
0 |
||
| H215M/AS332 |  |
🇩🇪 🇫🇷 | 1978 | 8 | 0 |
0 |
||
| AW139 |  |
🇬🇧 🇮🇹 | 2003 | 4 | 0 |
0 |
||
| AW609 |  |
🇮🇹 🇺🇸 | 2020 | 0 | 0 |
3 |
||
| Cessna 208 |  |
🇺🇸 | 1984 | 13 | 0 |
0 |
||
| DHC-6 |  |
🇨🇦 | 1966 | 10 | 0 |
0 |
